what is interpretable machine learning? view markdown
Modern machine learning (ML) models, particularly deep neural networks, are difficult to understand and explain. This has consequences when these networks are used to make critical decisions. Thus it is important to develop methods that can interpret these highly complex models. As ML models enter into high-stakes fields, interpretability will become increasingly important.
Interpretable ML as a field is still fairly immature, with many still asking the basic question “what is interpretability?”. One of our recent works aims to address this problem and understand the current landscape of the field of interpretable ML.
desiderata
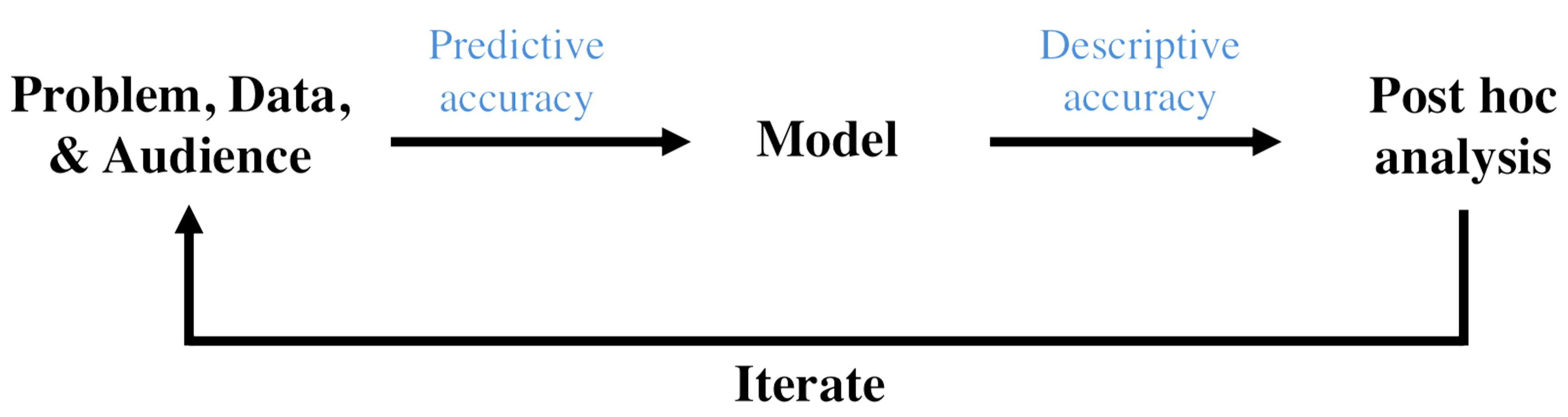
The work introduces three desiderata a good interpretable ML pipeline should satisfy: predictive accuracy, descriptive accuracy, and relevancy. These are depicted in a typical data-science lifecycle below.
methods
The work also categorizes existing methods into two main categories: model-based interpretability (i.e. the construction of models that readily provide insight into the relationships they have learned) and post-hoc interpretability (i.e. methods that analyze a trained model in order to provide insights into the learned relationships).
some examples
We have also been working on a line of work focused on understanding and using interactions in post-hoc interpretability:
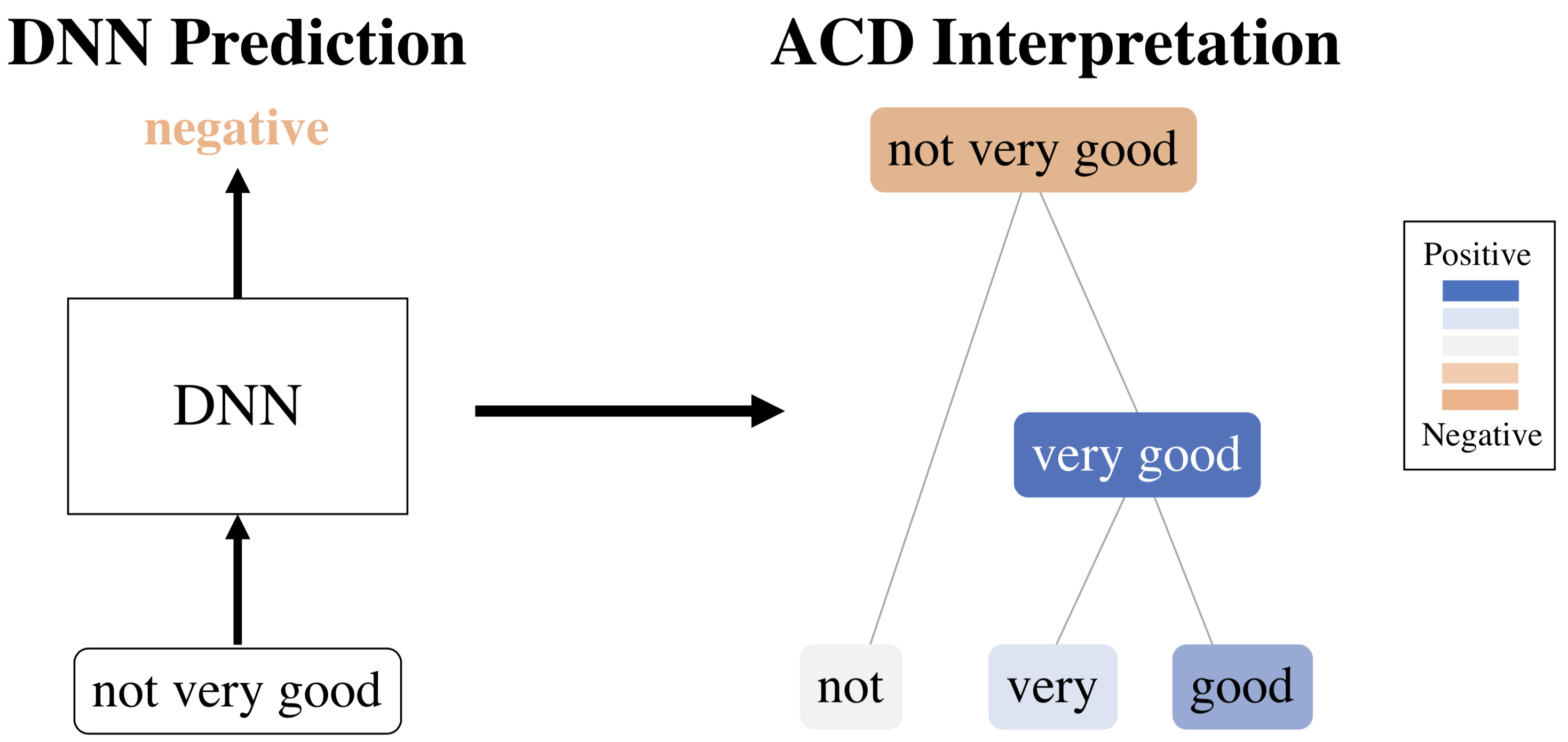
- ACD is an algorithm for generating hierarchical interpretations of a single prediction made by a neural network. It is able to score interactions for arbitrary DNNs by extending the Contextual Decomposition score and then hierarchically aggregate them into a succinct visualization
- CDEP penalizes interpretations of a DNN during training in order to incoporate prior knowledge and improve the predictive accuracy of models
- DAC extracts interactions from a fully trained random forest and visualizes these importances in the form of a curve or a heatmap
- TRIM attributes importance to different transformations of the input to any trained model